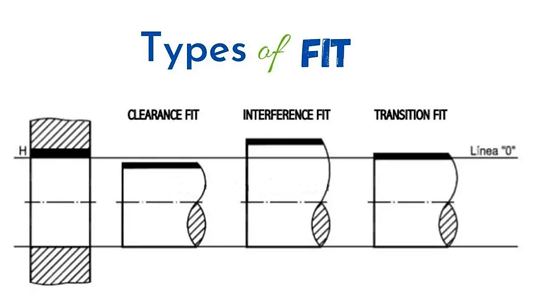
The three types of fit are:
1. Clearance: The hole is larger than the shaft, enabling the two parts to slide and / or rotate when assembled.
2. Location / transition: The hole is fractionally smaller than the shaft and mild force is required to assemble / disassemble
3. Interference: The hole is smaller than the shaft and high force and / or heat is required to assemble / disassemble
Clearance fits
| Category | Description and usage | Example fit |
| Loose running | Larger clearance where accuracy is not essential – e.g. pivots, latches, parts affected by corrosion, heat, or contamination | H11/c11 |
| Free running | Large clearance where accuracy is not essential and involves high running speeds, large temperature variations, or heavy journal pressures | H9/d9 |
| Easy running | Moderate clearances with minimal requirements for accuracy – e.g. high running speeds, large temperature variations, high journal pressures, long shafts, pump or fan bearings | H9/e9 |
| Close running | Small clearances with moderate requirements for accuracy – e.g. moderate running speeds and journal pressures, shafts, spindles, sliding rods | H8/f7 |
| Sliding | Minimal clearances for high accuracy requirements, which can be easily assembled and will turn & slide freely – e.g. guiding of shafts, sliding gears, crankshaft journals | H7/g6 |
| Location | Very close clearances for precise accuracy requirements, which can be assembled without force and will turn & slide when lubricated – e.g. precise guiding of shafts | H7/h6 |
For example, using an H8/f7 close-running fit on a 50 mm diameter:[1]
· H8 (hole) tolerance range = +0.000 mm to +0.039 mm
· f7 (shaft) tolerance range = −0.050 mm to −0.025 mm
· Potential clearance will be between +0.025 mm and +0.089 mm
Transition fits
| Category | Description and usage | Example fit |
| Tight fit | Negligible clearances which can be assembled or disassembled by hand – e.g. hubs, gears, pulleys, bushings, frequently removed bearings | H7/j6 |
| Similar fit | Negligible clearance or interference fit which can be assembled or disassembled with a rubber mallet – e.g. hubs, gears, pulleys, bushes, bearings | H7/k6 |
| Fixed fit | Negligible clearance or small interference fit which can be assembled or disassembled with light pressing force – e.g. plugs, driven bushes, armatures on shafts | H7/n6 |
For example, using an H7/k6 similar fit on a 50 mm diameter:[1]
· H7 (hole) tolerance range = +0.000 mm to +0.025 mm
· k6 (shaft) tolerance range = -0.018 mm to +0.002 mm
· Potential clearance / interference will be between +0.043 mm and −0.002 mm
Interference fits
| Category | Description and usage | Example fit |
| Press fit | Light interference which can be assembled or disassembled with cold pressing – e.g. hubs, bearings, bushings, retainers | H7/p6 |
| Driving fit | Medium interference which can be assembled with hot pressing or cold pressing with large forces – e.g. permanent mounting of gears, shafts, bushes (tightest possible with cast iron) | H7/s6 |
| Forced fit | High interference shrink fit requiring large temperature differential of parts to assemble, permanent coupling of gears and shafts that cannot be disassembled without risking destruction | H7/u6 |
For example, using an H7/p6 press fit on a 50mm diameter:
· H7 (hole) tolerance range = +0.000 mm to +0.025 mm
· p6 (shaft) tolerance range = +0.042 mm to +0.026 mm
· Potential interference will be between −0.001 mm and −0.042 mm.