The analyses of surface finish being carried out by
1. The average roughness method.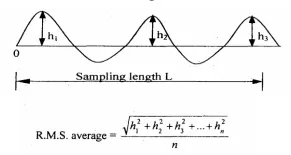
2. Peak to valley height method
3. From factor
1. Average roughness measurement
The assessment of average roughness is carried out by
a Centre line average (CLA).
b Root mean square (RMS)
c Ten point method
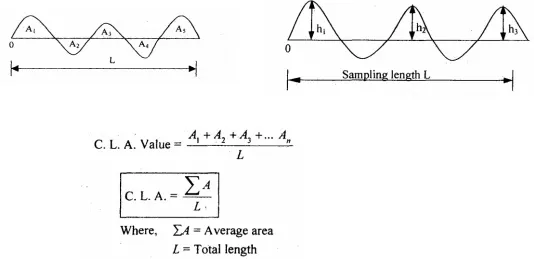
a. C.L.A. method
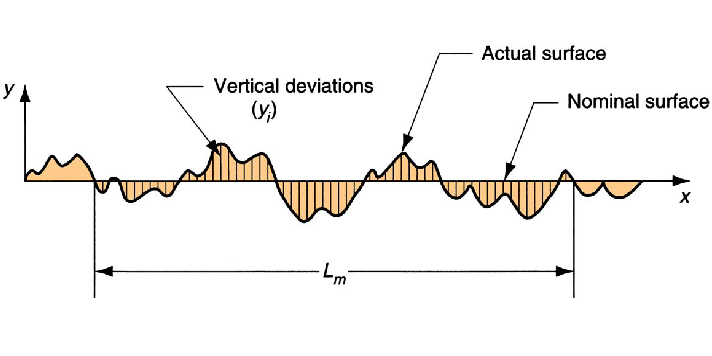
The surface roughness is measured as the average deviation from the nominal surface.
b. R.M.S. method
The roughness is measured as the average deviation from the nominal surface. Let, h1,h2, … are the heights of the ordinates and L is the sampling length
c. Ten point height method
The average difference between five highest peaks and five lowest valleys of surface is taken and irregularities are calculated by
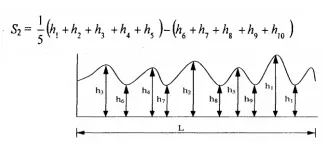
2. Peak to valley height method
Peak to valley height measures the maximum depth of the surface irregularities over a given sample length and largest value of the depth is accepted for the measurement.
Here, = Maximum peak to valley height in one sampling lengths. R = Maximum peak to valley height
V=Valley
P = Peak
Here, R is the maximum peak to valley height within the assessment length and the disadvantages of R, and is only a single peak or valley which gives the value is not a true picture of the actual profile of the surface
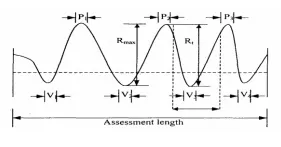
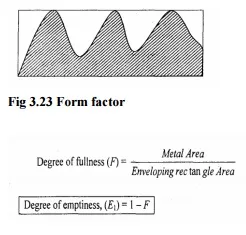
3. Form factor
It is obtained by measuring the area of material above the arbitrarily chosen base line in the section and the area of the enveloping rectangle.