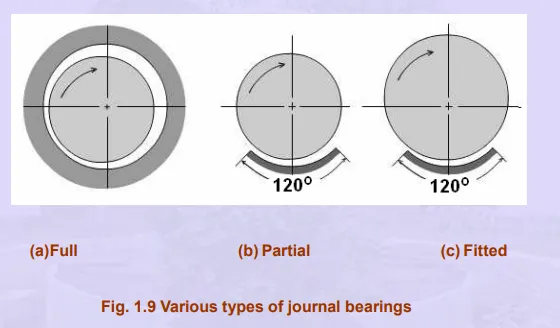
Among the sliding contact bearings radial bearings find wide applications in industries and hence these bearings are dealt in more detail here. The radial bearings are also called journal or sleeve bearings. The portion of the shaft inside the bearing is called the journal and this portion needs better finish and specific property. Depending on the extent to which the bearing envelops the journal, these bearings are classified as full, partial and fitted bearings.As shown in Fig.1.9
Hydrodynamic lubrication
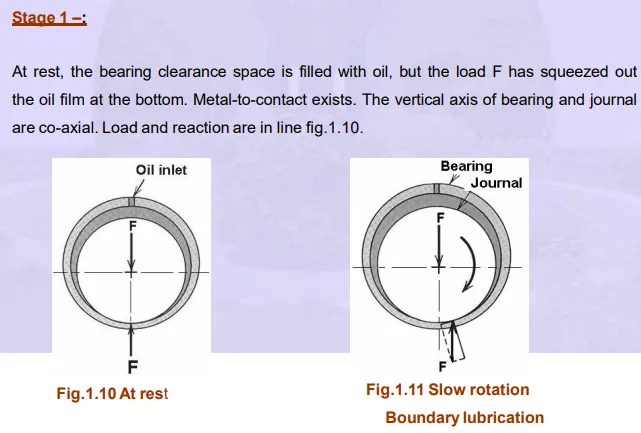
In 1883 Beauchamp Tower discovered that when a bearing is supplied with adequate oil, a pressure is developed in the clearance space when the journal rotates about an axis that is eccentric with the bearing axis. He exhibited that the load can be sustained by this fluid pressure without any contact between the two members
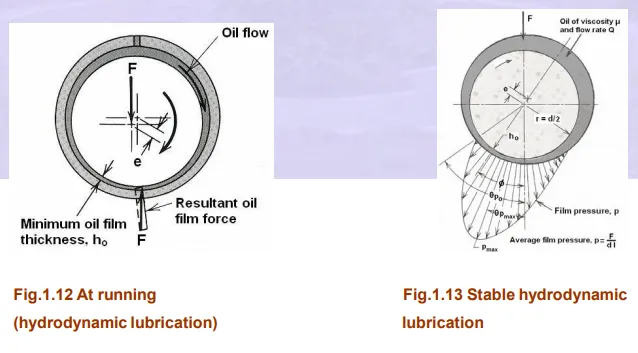
The load carrying ability of a hydrodynamic bearing arises simply because a viscous fluid resists being pushed around. Under proper conditions, this resistance to motion will
develop a pressure distribution in the film that can support useful load. Two mechanisms responsible for this are wedge film and squeeze film action. The load supporting pressure in hydrodynamic bearings arises from either (1) the flow of a viscous fluid in a converging channel, the wedge film, or (2) the resistance of a viscous fluid to being squeezed out from the between approaching surface, the squeeze film
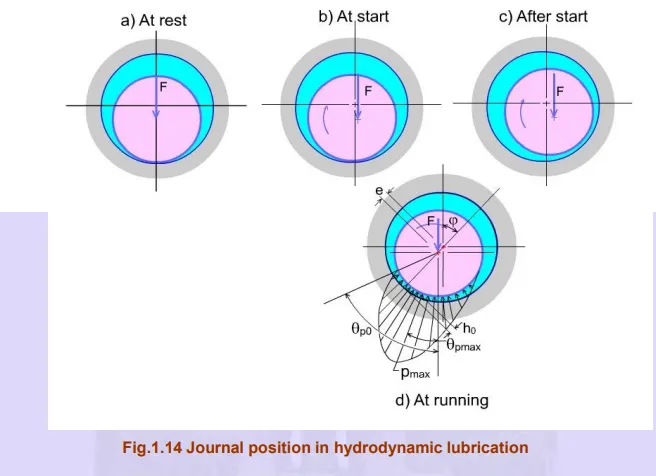
Stages in hydrodynamic lubrication
Consider a steady load F, a fixed bearing and a rotating journal.


HYDRODYNAMIC LUBRICATION – ANIMATION
The various stages of lubrication explained in 1.5.1 can now be perceived from the animation illustrated here.
The friction characteristics of hydrodynamic lubrication of journal bearings
The friction behaviour during hydrodynamic condition is shown in Fig.1.15 and the bearing will operate between point C and D under hydrodynamic lubrication condition. It can be seen from the graph Fig.1.15 and bearing modulus (μn / p) that








Comments are closed