Generators onboard ships are the power suppliers for the entire vessel and are the primary sources of power to all running machinery systems, including the propulsion plant. For this reason, safe and efficient running of the ship’s generator has to be given highest consideration. Two important safety measures of generators are: Preferential trips and Air Circuit Breaker (ACB).
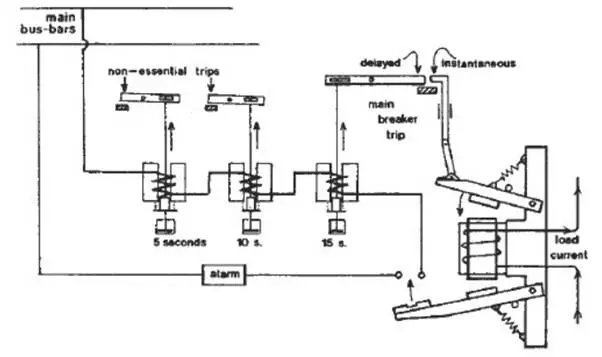
Preferential trip is a kind of electrical arrangement, which is designed to disconnect the non-essential circuit i.e. nonessential load from the main bus bar in case of partial failure or overload of the main supply.
The non-essential circuits or loads on ships are air conditioning, exhaust and ventilation fans, and galley equipment, which can be disconnected momentarily and can be connected again after fault finding. The main advantage of preferential trip is that it helps in preventing the operation of main circuit breaker trip and loss of power on essential services, thus blocking blackout and overloading of generators.
Construction and Working
The preferential trip circuit consists of an electromagnetic coil and a dashpot arrangement to provide some delay to disconnect the non-essential circuits. Along with this, there is also an alarm system provided, which functions as soon as an overload is detected and the trips start operating.
There are some mechanical linkages, which instantaneously operate and complete the circuit for preferential trips. The dashpot arrangement consists of a
piston, with a small orifice, placed inside a small cylinder assembly. This piston moves up against the fluid silicon and the orifice in the piston governs the time delay.
Working of Preferential Trip
The current passes through the electromagnetic coil and the linkages are kept from contacting using a spring arrangement.
As soon as the current value increases the limit, the electromagnetic coil pulls the linkage up against the spring force and operates the instantaneous circuit and the alarm system. The lower linkage completes the circuit for the preferential trip.
The current passes through the coil in the preferential trip circuit, which pulls the piston in the dashpot arrangement. The movement of this piston is governed by the diameter of the orifice and the time delay made by the same.
The preferential trip operates at 5, 10 and 15 seconds and the load is removed accordingly. If the overload still persists, then an audible and visual alarm is sounded. The preferential trip is one of those important electrical circuits, which help in removing the excessive load from the main bus bar, thus preventing situation like blackout especially when the ship is sailing in restricted or congested waters.
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)
Air circuit breaker is designed to overcome the defects and safeguard the machine before it breakdowns.
The main function of air circuit breaker is to:
· Open and close a 3 phase circuit, manually or automatically
· Open the circuit automatically when a fault occurs. Faults can be of various types – under or over voltage, under or over frequency, short circuit, reverse power, earth fault etc.
The main feature of ACB is that it dampens or quenches the arcing during overloading.
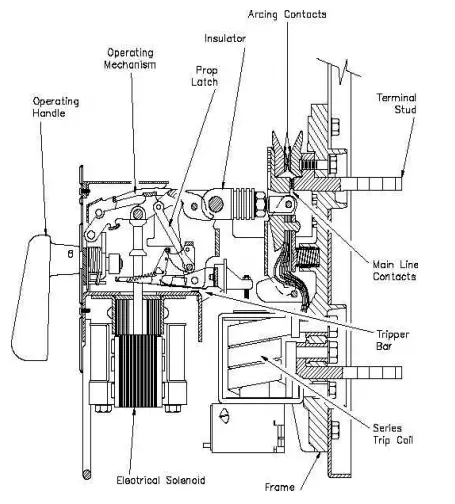
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) Construction & Working
ACB has two sets of contacts i.e. main and auxiliary contacts. Each set of contact consists of a fixed contact and a moving contact.
The main contact normally carries most of the load current. All the contacts are made of cadmium-silver alloy, which has good resistance to damage by arcing.
When the ACB is closed, the powerful spring is energized and the ACB is then latched shut against spring pressure. The auxiliary contact makes first & breaks last i.e. when ACB is closed, the auxiliary contact closes first and then the main contact follows.
When the ACB is open, the main contact open firsts and then the auxiliary contact opens. Thus the auxiliary contacts are subjected to arcing during the opening of ACB and can easily be replaced.
The main contact closing pressure is kept high so that the rise in the temperature in the contacts while carrying current remains within limits.
Closing coil operating on D.C voltage from a rectifier is provided to close the circuit breaker by operating a push button.
How Arc Quenching is achieved?
Quenching of arc is achieved by:
1) Using arcing contacts made of resistance alloy and silver tips for the main contacts. Arcing contacts close earlier and open later than the main contacts.
2) When opening contacts have travelled at high speed to stretch the resultant arc, which is transferred to the arcing contact.
3) Cooling and splitting of the arc is done by arc chutes, which draw the arc through splitters by magnetic action and quickly cools and splits the arc until it snaps. The circuit breaker opens when the arc is quenched.



Comments are closed