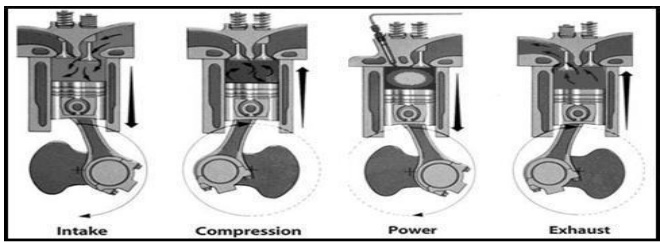
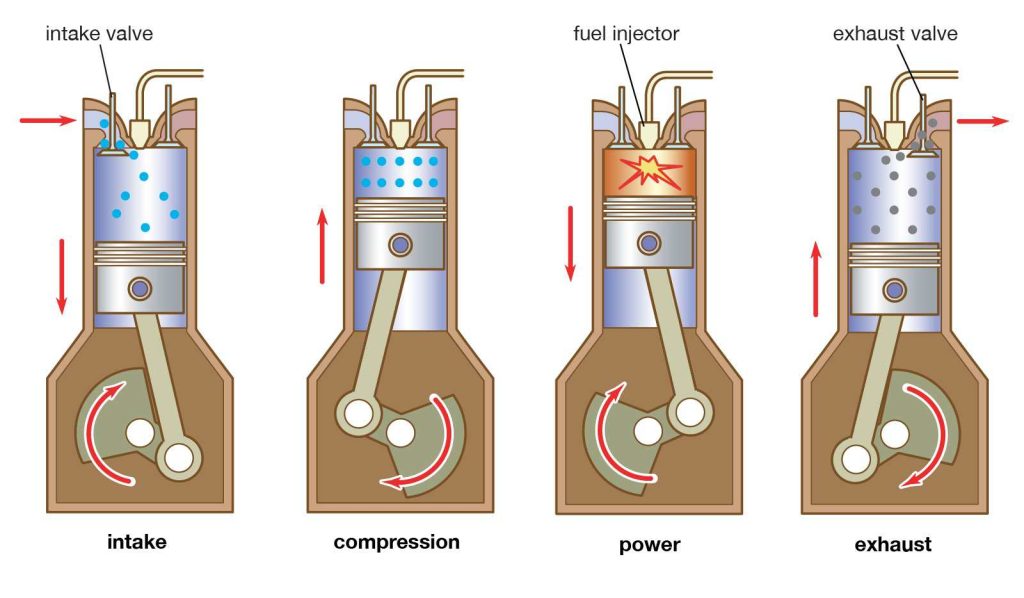
Construction:
• A piston reciprocates inside the cylinder
• The piston is connected to the crankshaft by means of a connecting rod and crank.
• The inlet and exhaust valves are mounted on the cylinder head.
• A fuel injector is provided on the cylinder head
• The fuel used is diesel.
(a) Suction Stroke (First Stroke of the piston)
• Piston moves from TDC to BDC
• Inlet valve is opened and the exhaust valve is closed.
• The pressure inside the cylinder is reduced below the atmospheric pressure.
• Fresh air from the atmosphere is sucked into the engine cylinder through air cleaner and inlet valve.
(b) Compression stroke (Second stroke of the piston)
• Piston moves from BDC to TDC
• Both inlet and exhaust valves are closed.
• The air is drawn during suction stroke is compressed to a high pressure and temperature
(c) Working or power or expansion stroke (Third stroke of the piston)
• The burning gases (products of combustion) expand rapidly.
• The burning gases push the piston move downward from TDC to BDC
• This movement of piston is converted into rotary motion of the crank shaft through connecting rod.
• Both inlet and exhaust valves are closed.
(d) Exhaust Stroke (Fourth stroke of the piston)
• Piston moves from BDC to TDC
• Exhaust valve is opened the inlet valve is closed.
• The burnt gases are forced out to the atmosphere through the exhaust valve. (some of the burnt gases stay in the clearance volume of the cylinder)
• The exhaust valve closes shortly after TDC
• The inlet valve opens slightly before TDC and the cylinder is ready to receive fresh air to start a new cycle.

Comments are closed