PETROL ENGINES
Classification of Petrol Engines
• Two Stroke cycle Petrol Engines
• Four Stroke cycle petrol Engines
FOUR STROKE CYCLE PETROL ENGINES
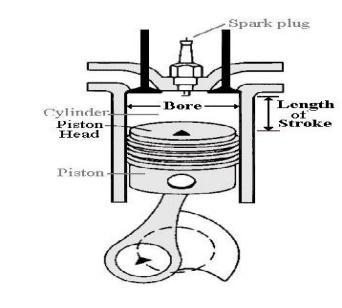
Construction :
• A piston reciprocates inside the cylinder
• The piston is connected to the crank shaftby means of a connecting rod and crank.
• The inlet and exhaust valves are Mounted on the cylinder head.
• A spark is provided on the cylinderHead.
• The fuel used is petrol
Four Stroke Petrol Engine- Working
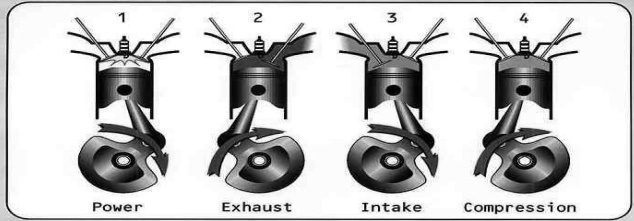
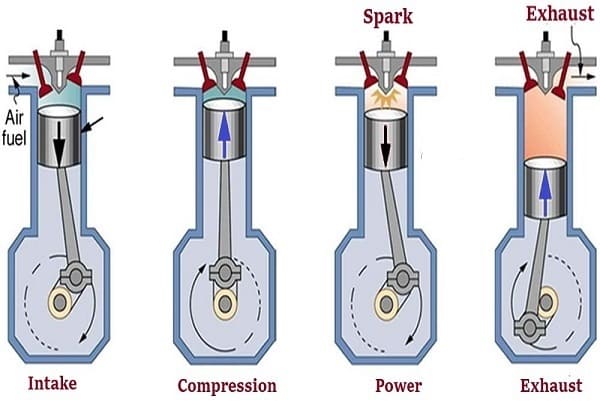
(a) Suction Stroke (First Stroke of the Engine)
• Piston moves down from TDC to BDC
• Inlet valve is opened and the exhaust valve is closed.
• Pressure inside the cylinder is reduced below the atmospheric pressure.
• The mixture of air fuel is sucked into the cylinder through the inlet valve.
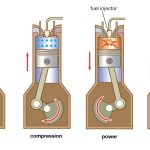
(b) Compression Stroke : (Second Stroke of the piston)
• Piston moves up from BDC to TDC
• Both inlet and exhaust valves are closed.
• The air fuel mixture in the cylinder is compressed.
(c) Working or Power or Expansion Stroke: (Third Stroke of the Engine)
• The burning gases expand rapidly. They exert an impulse (thrust or force) on the piston. The piston is pushed from TDC to BDC
• This movement of the piston is converted into rotary motion of the crankshaft through connecting rod.
• Both inlet and exhaust valves are closed.
(d) Exhaust Stroke (Fourth stroke of the piston)
• Piston moves upward from BDC
• Exhaust valve is opened and the inlet valve is closed.
• The burnt gases are forced out to the atmosphere through the exhaust valve (Some of the burnt gases stay in the clearance volume of the cylinder)
• The exhaust valve closes shortly after TDC
• The inlet valve opens slightly before TDC and the cylinder is ready to receive fresh charge to start a new cycle.
Summary :
• Compression ratio varies from 5 to 8
• The pressure at the end of compression is about 6 to 12 bar.
• The temperature at the end of the compression reaches 250o C to 350o C
Comments are closed