TWO STROKE CYCLE DIESEL ENGINES- CONSTRUCTION
Construction :
• Two stroke cycle diesel engines require air supply
• This air is used to blow out the exhaust gases and to fill the cylinder with clean air
• This air is supplied by a blower or air compressor which is driven by engine itself.
• These engines may be valve or port type.
• A plate is provided in the crank case to admit air into the crank case.
• Transfer and exhaust ports are provided in the cylinder.
• These ports are covered and uncovered by the moving piston.
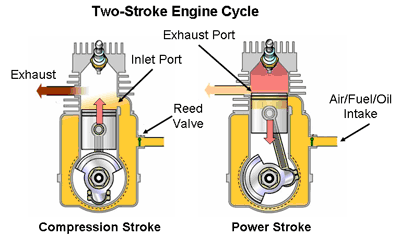
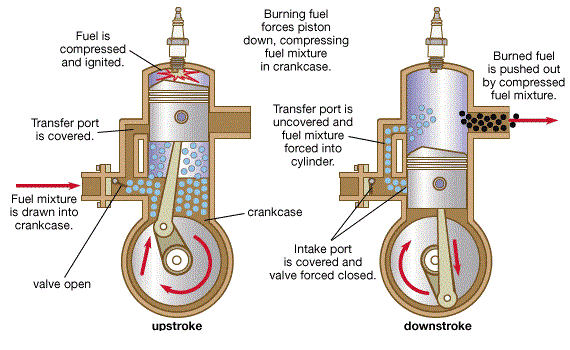
First Stroke (Upward Stroke of the piston)
(a) Compression and inductance:
• The piston moves upwards from Bottom Dead Centre (BDC) to Top Dead Centre (TDC).
• Both transfer and exhaust ports are covered.
• Air which is transferred already into the engine cylinder is compressed by moving piston.
• The pressure and temperature of the air increases.
• At the same time, fresh air is admitted into the crankcase through the plate valve (reed valve)
First Stroke (Upward Stroke of the piston)
(b) Ignition and inductance.
• Piston almost reaches the top dead centre.
• The fuel is injected into the hot compressed air inside the cylinder. The fuel mixed with hot air and burns.
• The admission of fresh air into the crankcase continues till the piston reaches the top centre.
Second Stroke (Downward Stroke of the piston)
(c) Expansion and crank case compression:
• The burning gases expand in the cylinder.
• Burning gases force the piston to move down. Thus useful work is obtained.
• At the same time, the air in the crank case is compressed by the movement of piston.
• All the ports and the plate valve are in closed position
Second Stroke (Downward Stroke of the piston)
(d) Exhaust and Transfer:
• At the end of expansion, the exhaust port is uncovered.
• The burnt escape to the atmosphere through the exhaust port.
• Transfer port is also uncovered shortly after the exhaust port is opened.
• The partially compressed air from crank case enters the cylinder the transfer port.
• This air is deflected upwards by the deflected shape of the piston.
• Thus the entering air helps in forcing out the combustion products from the cylinder
• The plate valve remains during this period.
Comments are closed