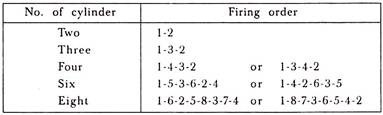
Supercharging is the name given to the process of increasing the pressure of the air-fuel mixture entering a petrol engine to a pressure greater than that of atmospheric air and is achieved usually by means of a small compressor or blower called a supercharger. Superchargers also whirl the mixture into a more homogeneous state.
The power required to drive superchargers or blowers is taken from the engine through gears. Superchargers are used to increase the capacity of an existing engine or to bring the reduction in size of the engine for the same output or to restore the normal sea power of the engine when it is running at high altitudes.
It has been found that by supercharging the petrol engine to twice the atmospheric pressure the power is more than doubled and the same degree of supercharging in compression ignition engines increases their output by about 75%.
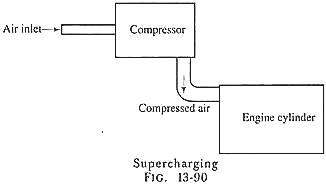
The firing order of the engine is a sequence in which the multi-cylinder engines are fired. In the multi-cylinder engine, the engines are fired not in the normal sequence but they are fired in different sequences. The firing order is maintained for proper balancing of the engine and adjustment of the unbalanced forces. The firing order indicate the sequence in which the cylinders are fired. The number of cylinder is written in sequence.
The following table shows firing order of different engines: