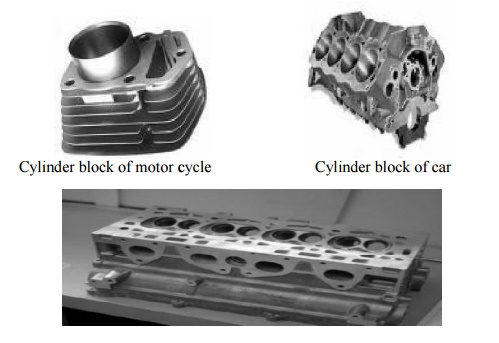
Cylinder Block:
• It is the main block of the engine.
• It contains cylinders accurately finished to accommodate pistons
• The cylinder block houses crank, camshaft, piston and other engine parts.
• In water cooled engines, the cylinder block is provided with water j ackets for the circulating cooling water.
• The materials used for cylinder are grey cast iron, aluminium alloys etc.,
• It is usually made of a single casting
Cylinder block of motor cycle Cylinder block of car
Cylinder Head:
• The cylinder head is bolted to the cylinder Block by means of studs.
• The water jackets are provided for cooling water circulation.
• The materials used for cy linder head are cast iron, aluminium alloy etc.,
• This is also generally made of single cast iron.
Cylinder Liners:
• The liner is a sleeve whi ch is fitted into the cylinder bore.
• It provides wear resisting surface for the cylinder bores.
Liners are classified into:
• (a) Wet liner (b) Dry liner
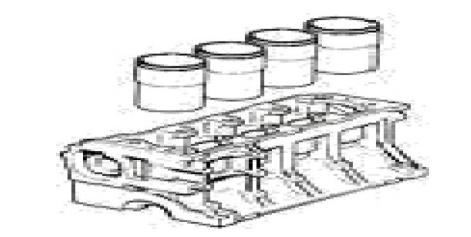
Cylinder Liners
Wet Liner : These liners are surrounded or wetted by cooling water. It provides wear resisting surface for the piston to reciprocate. Also it acts as a seal for the water jacket
Dry Liner :Dry liners have metal to metal contact with the cylinder block. They are not directly in touch with the cooling water.
Liner Materials:
• Liner material should withstand abrasive wear and corrosive.Chromium plated mild teel
• tubes are used as liners.

Crankcase : It may be cast integral with the cylinder
block.Some times, it is cast separately and then attached to the block. These materials are used for crank case are cast iron, aluminium alloys or alloy steels.
Oil pan or oil sump:
Oil sump is the bottom part of the engine.It contains lubricating oil.A drain plug is provided the oil sump to drain out the oil.It is made of the pressed sheet.
Piston :
The piston serves the following purposes
• It acts as a movable gas tight seal to keep the gases inside the cylinder
• It transmits the force of explosionin the cylinder to the crankshaft through the connecting rod.
• Some of the materials used for piston are cast iron, aluminium alloy, chrome nickel alloy, nickel iron alloy and cast steel.

Piston rings :
Piston rings are inserted in the grooves provided in the piston. Two types of piston rings are used in the piston.
1. Compression rings
2. Oil rings or oil control rings

MAIN COMPONENTS OF IC ENGINE
(Piston Rings (Compression and Oil rings)

Compression rings :
• Compression rings provide an effective seal for the high pressure gases inside the cylinder.
• They prevent the leakage of high pressure gases from the combustion chamber into the crank case.
• Each piston is provided with at least two compression rings.
Oil rings :
• Oil rings wipe off the excess oil from the cylinder walls.
• It also returns excess oil to the oil sump, through the slots provided in the rings. The materials used for piston rings should be wear resistant.
Normally piston rings are made of alloy steel iron containing silicon, manganese alloy steels etc.
Connecting Rod:
• It connects the piston and crank shaft.
• It transmits the force of explosion during power stroke to the crankshaft.
• The connecting rod has bearings at both ends.
• The small end of the connecting has a solid or split eye and contains a bush.
• This end is connected to the piston by means of a gudgeon pin.
• The other end is called as big end of the connecting rod.
• The connecting rods must withstand heavy thrusts.
• Hence it must have strength and rigidity.
• They are usually drop forged I sections.
• The materials used are plain carbon steel, aluminium alloys, nickel alloy steels etc,
Crank Shaft :
• It is the main rotating shaft of the engine.
• Power is obtained from the crank shaft.
• The crank shaft is combination with connecting rod converts reciprocating motion of the piston into rotary motion.
• The crank shaft is held in position by the main bearings.
• There are two main bearings to support the crank shaft.
• The materials used for crank shaft are billet steel, carbon steel, nickel chrome and other heat treated alloy steels.
Camshaft:
• Camshaft contains number of cams.
• It is used to convert rotary motion into linear or straight line motion.
• It has so many cams as the number of valves in an engine.
• An additional cam is also provided to drive the fuel pump.
• A gear is provided in the cam shaft to drive the distributor or oil pump.
The opening and closing of the engine valves are controlled by the cams provided on the cam shaft.


