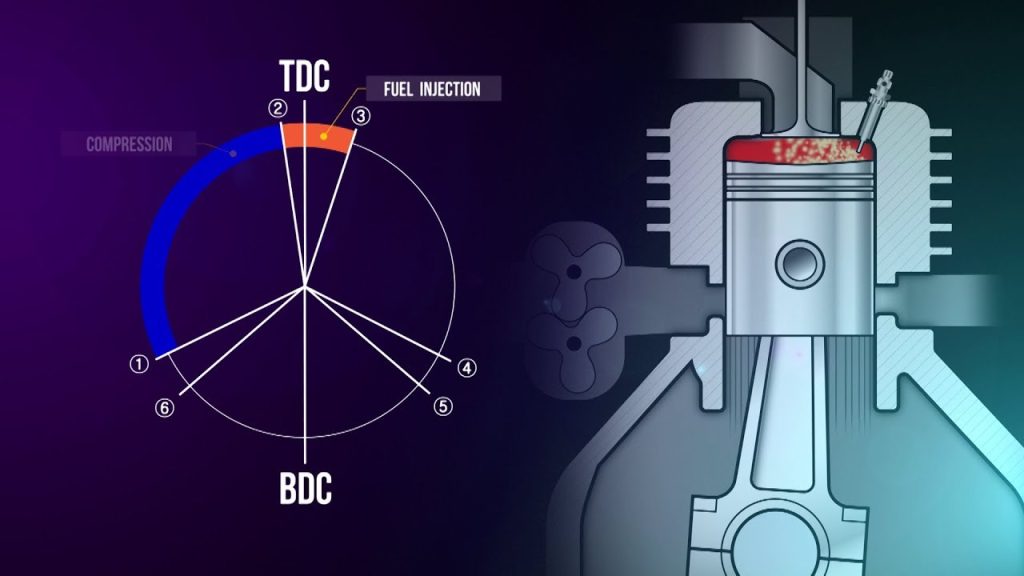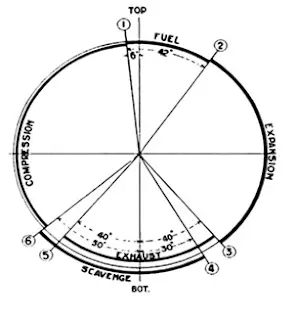
Above: Timing Diagram for a 2-stroke Engine Cycle
| Stages | Piston Motion | Temp. Of Compressed Air(°C) | Pressure of Compressed Air (Bar) | Exhaust Valve | Scavenge Port |
| Compression | Upwards | 550 | 80-90 | Closed | Covered |
| Combustion | Downwards | – | – | Closed | Covered |
| Expansion | Upwards | 1700 | 130-160 | Closed | Covered |
| Exhaust & Scavenge | Downwards | – | – | Open | Uncovered |
Compression Stroke:
· Fresh air is compressed from BDC to TDC (80-90bar) with its temperature raised to around 550°C.
· Scavenge port are just covered, exhaust valve is closed and fuel injector is shut.
Combustion stroke:
· Fuel oil is injected into the hot air, igniting it.
Combustion Period
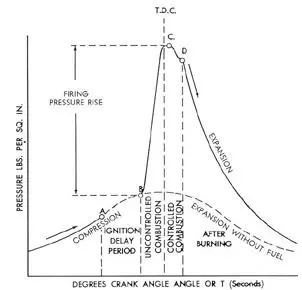
Rapid Combustion Period:
· Between injection and the start of ignition.
· Initial droplets enters the cylinder are being heated up by the surrounding charge air and starts to vapourise and ignite.
Rapid Combustion Period:
· Fuel that was accumulated during the ignition delay period starts to burn rapidly due to the pre-mixed combustion.
· This period will be accompanied by a sharp rise in cylinder pressure and fuel injection still continues during this period.
Steady Burning Period:
· Combustion has been achieved and the fuel entering the cylinder will burn as soon as they have penetrated, heated, mixed and vapourised.
· Cylinder pressure rises to its maximum value just after TDC, near the middle of the steady combustion period, and decreases gradually before expansion stroke begins.
After Burning Period:
· Combustion continues until the remaining fuel is burnt despite the fact that the injection stops.
Expansion Stroke:
· After combustion, the air pressure goes up to 130-160bar with its temperature reaching to about 1700°C.
· Piston is pushed downwards by the force from the expansion of gases.
· Gases fall in pressure as they expand.
Exhaust & Scavenge:
· Exhaust valve open towards the end of expansion stroke.
· Due to differential pressure during blow-down period, exhaust gases are pushed out of the cylinder into exhaust manifold.
· Once scavenge ports are uncovered, the scavenge air pushes the remaining gases out of cylinder and filling it up with fresh air for the next cycle.