Concrete Structures are purely composed of concrete and is considered the safest mode of offshore industrial operations. They maybe directly fixed or molded to the sea floor on a permanent basis or maybe floating.
Fixed ones are also known as Gravity-based structures or the Caisson type. The entire structure is based on a submerged island-like solid structure which may serve as a foundation structure as well as storage or oil or other by-products. The entire load of the structure acts directly on the subsequent layers of the sea-bed eradicating problems even of the extreme wave disturbances or seafloor scour. On the other hand the floating ones are freely float-able and has six degrees of freedom under a proper mooring system.
Some designs of these concrete structures are Condeep, ANDOC, Doris and so on. The design parameters are guided by the number of supporting columns and the diameter of the legs. Constructing is a tedious process where the entire structure or its components are towed and assembled with proper ballasting and de-ballasting measures. They have almost negligible maintenance and high durability. Can be also used for greater depths.
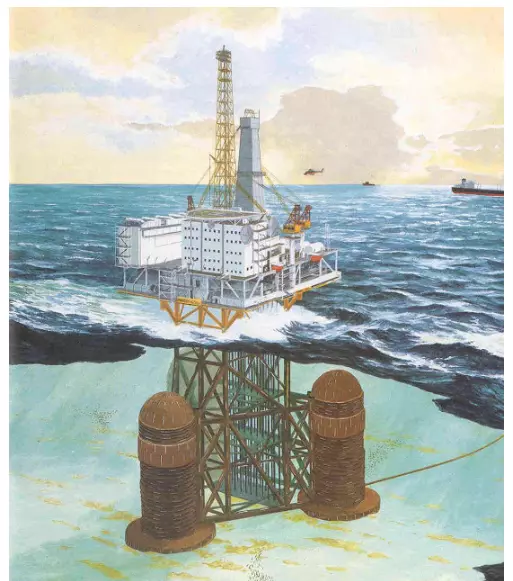
Fig.4: Garvity based Offshore Structure
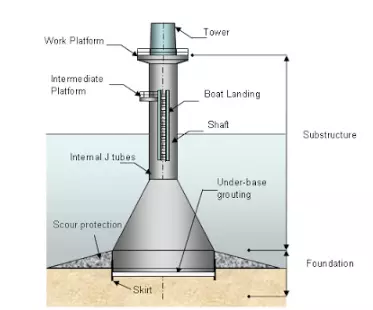
| Fig. 5: Concrete fixed platform |
Compliant Towers
Whenever the word “compliant” comes to our mind we mean a sense of complying or yielding. These are tall, slender, single isolated structures with high slenderness ratio.
They are comprised of specialized flex tubes of 2 to 7 metres in diameter comprising the space-time frame-like truss with high degrees of flexibility and can withstand high amounts of lateral loads up to 10 feet due to waves or oceanic disturbances.
The rig consists of narrow, flexible (compliant) towers and a piled foundation supporting a conventional deck for drilling and production operations. They are mainly operated in depths upto 1500 to 3000 feet. They inherently have a frequency lower than the natural frequency of the waves, such that with the emergence of any wave disturbance can make it oscillate with a resultant frequency safer for the loads and eradicate the probability of any resonating conditions. They work on a principle of de-amplification of waves dissipating the energy responsible for creating greater mayhem. Hence they are applicable for high tide or even the worst sea conditions.The lower part of the frame depends on the pilings and can penetrate hundreds of feet below the mud line.
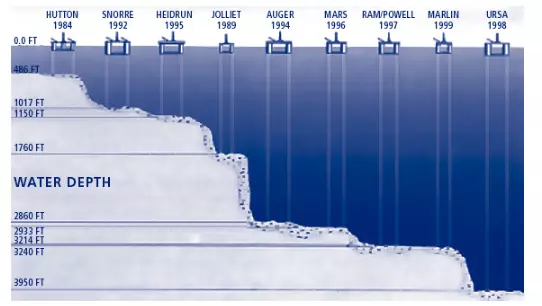
| Fig.6: Different Compliant Structures through the years |
Tension-Leg platforms
These are floating facilities which stay afloat and remain in position with the help of specialized steel tubes called tethers or tendons. These are nothing but the supporting legs of the floating platform which by the virtue of their upward tension takes care of the position, loading and the functionality of the extraction system. For all such tension leg platforms there is not much vertical oscillatory motion of the platform how rough the sea conditions or the average wave height may be. This facilitates in tying with the wellheads and the piping system for extraction of oil without much distortion. for all such systems there is always an additional buoyant force which keeps the platform afloat. Thus for all such installations,
Tension =Buoyancy – Weight
Here topside facilities and the basic parameters like the number of risers have to be fixed at pre-design stage. Generally the platform is manufactured on the shore and is towed to the desired location with the help of tugs. This structure is apt for depths up to 1200 metres and has limited or no storage facility. As of common usage, these have a high maintenance and surveillance cost of the tethers and under unavoidable circumstances the structure may be prone to irreversible damage.
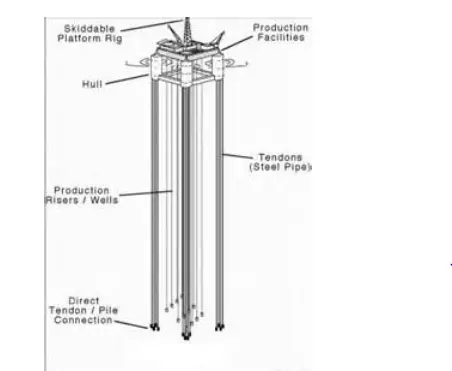
Fig. 7: Structure of a typical tension-leg platfrom.



Comments are closed