Introduction to Marine Diesel Firing Order
Marine main diesel engines can be two stroke or four stroke engines running on diesel or heavy fuel oil.
The firing order of these engines depends on the number of cylinders and the approach to vibration and fatigue taken by the engine designer and manufacturer.
This is an article on marine diesel engines and in particular the cylinder firing order. We begin with a recap of a typical two stroke engine operation, noting the components that have to be designed for the least vibration.
Ships Marine Diesel Engine Operation Overview
When I was a young ships engineer over 40 years ago, the diesel engine cylinders were numbered opposite from the normal car engine. The ships engine cylinders are numbered from the flywheel end of the engine, whereas car engine cylinders are numbered from the free end of the engine. I am sure the same numbering system is still in use today, but I will be corrected if not!
In this instance we shall look at the operation of a 6 cylinder Sulzer (6RD76) marine diesel engine, producing almost 10,000hp at 120 RPM. I was an engineer on this type of engine during my time at sea.
Sulzer has now merged with Wortsila, a Finish engineering company and have produced the world’s largest ships diesel engine. This is a 14 cylinder engine that when operating at 102 RPM produces over 108,000 hp.
Anyway back to our 6 cylinder engine that is started on compressed air. (At least three cylinders are required on a 2-stroke diesel for the engine to be able to start ahead or astern.) Once rotating at sufficient revolutions, the starting air supply is cut off and fuel is injected to the cylinders in the correct firing order.
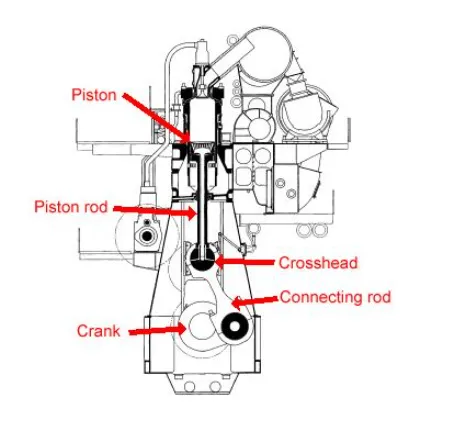
This combusts under compression and powers the piston downwards, the piston being connected to the piston rod. The piston rod is bolted to the top section of the crosshead bearing, the connecting rod being attached to the bottom section, rotates the crankshaft that is fully supported on white-metal main bearings.
On the upward stroke, the exhaust gasses are expelled through a rotating valve into the turbo blower exhaust turbine that drives a compressor/blower supplying combustion air to the scavenge ports and into the cylinder. The piston then returns to the top of its stroke and with the new charge of air, and combustion takes place again. A drawing from Wartsila-Sulzer is shown below depicting the main components that contribute to torsional vibration and can be minimized by balancing and selection of the correct firing order at the design stage.
So from above, the main components that add to torsional vibration are;
§ The piston.
§ Piston rod.
§ Crosshead bearing.
§ Connecting rod.
§ Crankshaft and bearings.
The Importance of Correct Firing Order to a Marine Diesel Engine
A ships diesel engine such as MAN, B & W, and Sulzer are all designed to have a firing order to meet the following requirements;
1. Engine Vibration
Torsional Vibration – caused by the reciprocating components, this is a highly undesirable condition in a marine engine. Not only for the comfort of passenger and crew, but also for the durability of the engine through undue fatigue.
2. Engine Balance
Imbalance of components is once again the cause of fatigue of the rotating components, especially the crankshaft. It is imperative that the firing order compliments not only the balancing of the components, but balances the power output from the cylinders spreading the load over the length of the crankshaft.
3. Gas Forces
Enormous gas forces are produced in the cylinders on the compression/firing stroke. These create individual cylinder torque characteristics that are transmitted downwards into the engine block, and bedplate via the main crankshaft bearings.
So these are the main reasons for the correct firing order in a marine diesel engine. Going back to the 6 cylinder Sulzer diesel engine I sailed on for a few years, I recollect the firing order to be 1,5,3,6,2,4.
Looking at some of the marine diesels on the web, the main engine manufacturers use various different firing orders that, as noted above, are crucial to the design of the ships marine diesel engines.


Comments are closed