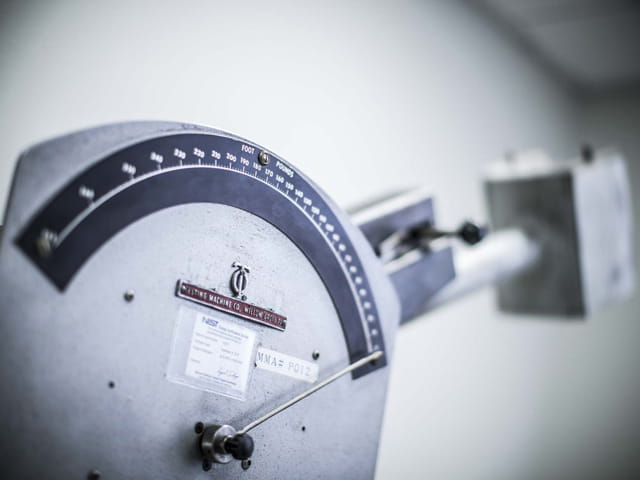
An impact blow is delivered to a test specimen by means of a pendulum-type hammer. The impact value of the material is determined from the energy required to break the specimen.
Testing method
| Testing method | Testable ranges | Test specimen | Data to be obtained | Corresponding standards |
| Charpy impact | Hammer capacity: 0.5,1,2,4,7.5,15J Test temp.: -40 – 150℃ Impact speed: 0.5~4J 2.9(±5%)m/sec 7.5J、15J 3.8(±5%)m/sec | 80.0±2×10.0±.02 ×4.0±0.2mmt n=5 | Fracture energy〔J〕 Impact strength〔kJ/m2〕 | JIS K7111-1 (ISO 179-1) JIS K6745 JIS K6911 |
| Izod impact | Hammer capacity: 1,2.75,5.5J 40,80,150kg・cm Test temp.: -40 – 150℃ Impact speed: 3.5(±10%)m/sec | 80.0±2×10.0±0.2 ×4.0±0.2mmt 63.5±0.5×12.7±0.1 ×2 – 13mmt n=5 | Fracture energy〔J〕 Impact strength〔J/m、kJ/m2〕 | JIS K7110 (ISO 180) ASTM D256 |
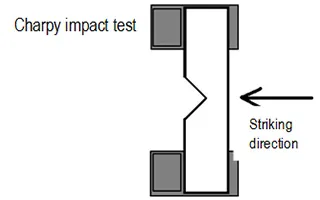
A test specimen having a V-shaped notch is placed on the holder in such position that the notched section is in the center of the holder, and the specimen is broken by striking the back of the notched section with the hammer. The fracture energy is determined from the swing-up angle of the hammer and its swing-down angle. The Charpy impact value (kJ/m2) is calculated by dividing the fracture energy by the cross-section area of the specimen.
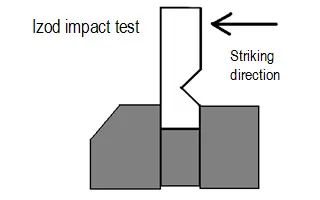
A test specimen having a V-shaped notch is fixed vertically, and the specimen is broken by striking it from the same side as that of the notch by the use of the hammer. The fracture energy is determined from the swing-up angle of the hammer and its swing-down angle. The Izod impact value (J/m, kJ/m2) is calculated by dividing the fracture energy by the width of the specimen.


